Our Core Services
Building a Business Sustainability Framework That Delivers Scalable Growth
Do you know why some companies remain successful for decades and others cannot sustain their momentum after achieving initial success? The reason is usually tied to how they manage business sustainability. Well-designed, a sustainability model becomes the pillar of long-term business performance, developing resilience to market changes while facilitating consistent growth.
Most businesses misconceive sustainability as mere environmental practices or mere financial solvency. The reality is more complex—business sustainability involves a comprehensive approach that weighs economic growth, environmental stewardship, and social responsibility while laying the groundwork for future growth.
Here on this page, we will see how to construct a business sustainability framework tailored to achieve scalable growth, dissecting the key elements, step-by-step implementation, and quantifiable benefits you will realize.

Table of Content
What is Business Sustainability?

Business sustainability is the conduct of running a business so that it is sustainable in the long term and grows while it achieves economic performance, environmental stewardship, and social responsibility. Business sustainability models are different from old-fashioned business models, which center on just short-term profit, as they include the triple bottom line: people, planet, and profit.
For small and medium-sized enterprises, sustainability is not only about minimizing environmental impact, but that’s definitely part of it. It’s about building systems that are resilient enough to help your business weather market cycles, respond to changing consumer needs, and grow operations effectively without exhausting resources or wrecking the reputation of your brand.
Consider business sustainability to be constructing a house on a firm foundation instead of one that appears excellent yet could crumble at the slightest pressure. The former takes more planning initially but is made to endure and grow if need arises.
Why Business Sustainability Matters for Your Brand
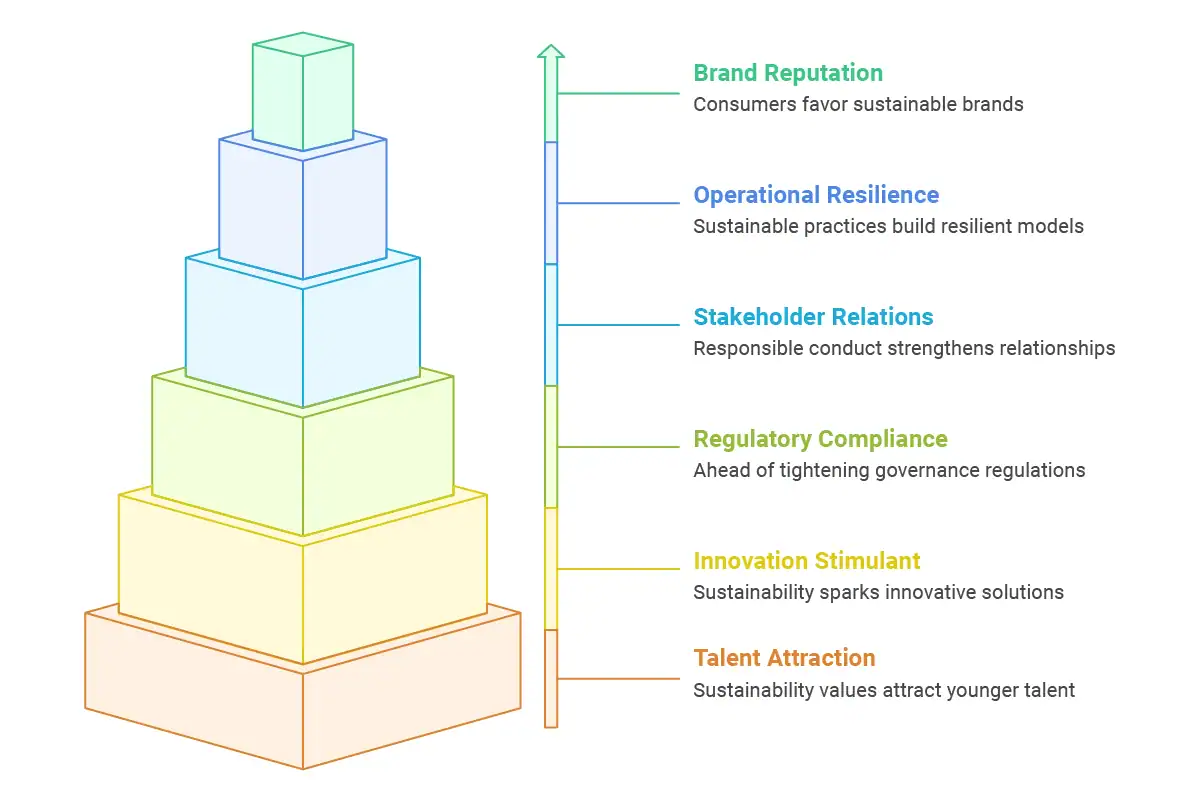
Having a robust sustainability system in place yields concrete advantages that immediately benefit your brand’s growth potential and market standing:
Increased brand reputation and trust
Consumers today increasingly favor companies that show a serious commitment to sustainable operations. A McKinsey study revealed that 70% of shoppers will pay more for sustainable and environmentally friendly brands.
Operational resilience
Condensing operations, eliminating waste, and increasing resource efficiency are all hallmarks of sustainable business practices that build more resilient business models capable of surviving economic slumps or supply chain interruptions.
Enhanced stakeholder relations
Investors, employees, and customers are all demanding that businesses conduct themselves responsibly. Delivering on these demands is what builds strong relations with these crucial stakeholders.
Regulatory compliance and risk avoidance
As environmental and social governance regulations are tightening across the world, sustainable companies are ahead of compliance, not risking fines and reputational harm.
Innovation stimulant
The limiting conditions of business sustainability often spark innovative problem-solving and innovation, leading to innovative products, services, or business models that can become sources of competitiveness.
Talent attraction and retention
Among younger generations, in particular, working for a firm with high sustainability values has become an important consideration in job choices. Firms with genuine sustainability systems generally experience increased employee commitment and turnover.
Core Components of a Growth-Oriented Sustainability Framework

An optimally effective business sustainability system is comprised of a number of interlinked elements. All of them are instrumental in developing a system that not only sustains responsible operation but also fuels scalable growth.
Strategic Alignment
The key to any good sustainability model is aligning with your overall business strategy. That is, sustainability is not considered an add-on initiative but is integral to your company’s mission, vision, and strategic goals.
For this element to be effective, leadership should decisively explain how sustainability initiatives align with business objectives and growth strategies. This may include redefining success metrics to incorporate sustainability indicators in addition to conventional financial indicators or recasting business challenges in terms of sustainability.
Firms that are successful at strategic development make their sustainability goals directly aligned with their competitive strategy and market differentiation, achieving harmony but not contradiction between growth and sustainability.
Resource Optimisation
Sustainable resource management is about maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste in all business operations—be it energy and materials, human capital, and financial resources.
This aspect entails:
- Carrying out resource audits to pinpoint inefficiencies
- Embracing circular economy principles wherever feasible
- Investing in resource-saving technology
- Educating personnel on resource-aware practices
- Establishing definite, quantifiable targets for reducing resources
Companies that undertake complete process analysis frequently find compelling opportunities for cost reduction as well as for sustainability enhancements, and this sets up a cycle where sustainability efforts end up driving profitability and growth potential.
Stakeholder Engagement
Sustainable companies acknowledge that they are part of a stakeholder ecosystem—employees, customers, suppliers, communities, and investors—whose support is essential to long-term success.
This element of the framework entails:
- Developing open lines of communication with all stakeholder groups
- Proactively soliciting stakeholders’ ideas on business sustainability opportunities
- Building partnership collaborations that benefit sustainability objectives
- Reporting periodically on sustainability progress and challenges
- Linking sustainability actions with stakeholder expectations and values
When executed effectively, stakeholder engagement converts future critics into allies and supporters, far increasing your brand’s reach and power and cutting resistance to growth initiatives.
Measurement and Governance
What is measured is what is managed. Strong sustainability systems consist of good systems for target setting, measuring performance, and holding the organisation to account for outcomes.
This element entails:
- Choosing suitable business sustainability key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Having a system for gathering data on sustainability measures
- Having governance arrangements with defined sustainability roles
- Having systems of incentives linked to sustainability goals
- Transparency and regular reporting of sustainability performance
With the right measurement and management, sustainability becomes a force for operational efficiency instead of a cost centre, facilitating instead of inhibiting scalable growth.
Partner With Us for a Greener Supply Chain
Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Sustainability Framework
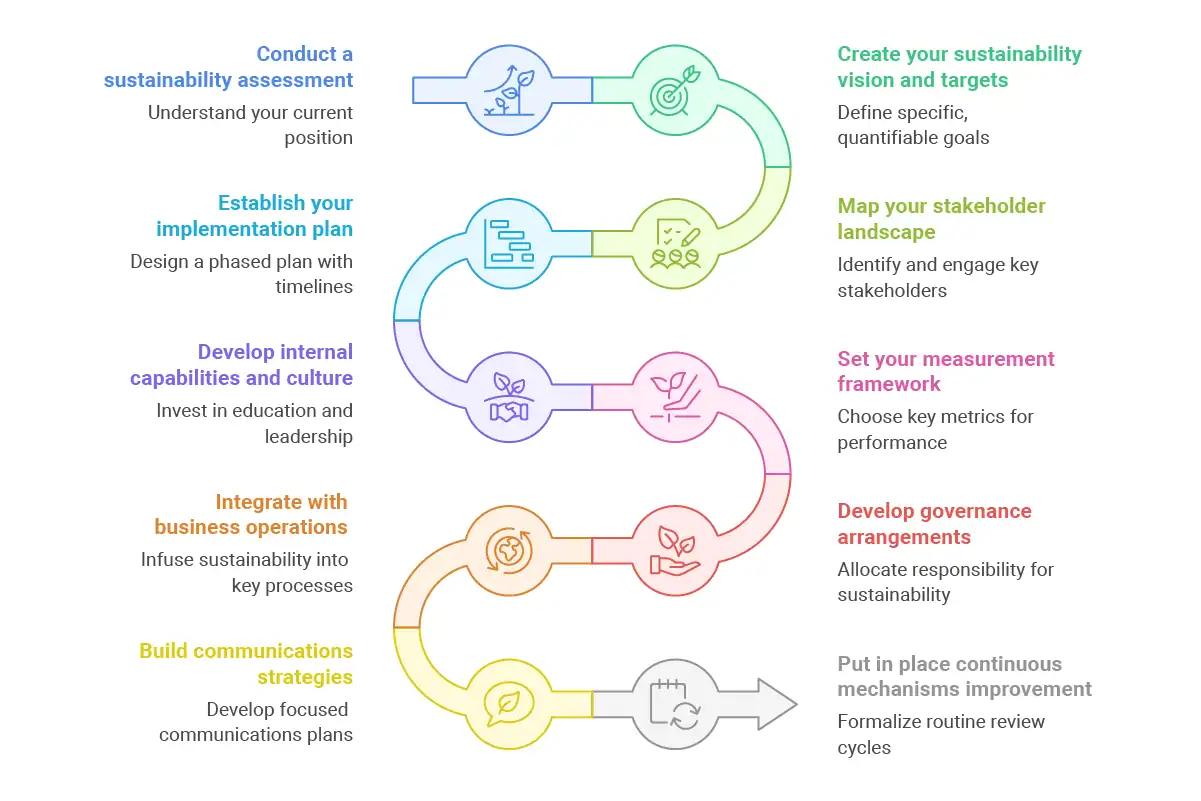
Developing a sustainability framework that genuinely supports business growth requires a systematic approach. Follow these steps to create a framework tailored to your business:
Conduct a sustainability assessment
Begin by understanding your current position. Assess your environmental impact, social practices, governance structures, and economic model. Identify strengths to build upon and gaps to address. This baseline will help measure progress and set realistic goals.
Create your sustainability vision and targets
Describe what sustainability is specifically to your business and how it relates to your growth plan. Establish specific, quantifiable targets that align with your business objectives and tackle your greatest impact areas.
Map your stakeholder landscape
Map out all the stakeholders impacted by or impacting your sustainability initiatives. Know their expectations, worries, and possible inputs. Prioritize engagement by importance to your sustainability agenda and business development.
Establish your implementation plan
Design a phased plan with specific programs, resource needs, responsibility, and timelines. Balance low-hanging fruit that creates momentum and longer-term architectural changes. Make the plan supportive of and not limiting to your growth path.
Develop internal capabilities and culture
New mindsets and skills are needed for sustainability. Invest in education, hire sustainability competency, and build leadership capacities that enable integrated decision-making. Strive to infuse your organisational culture with sustainability thinking.
Set your measurement framework
Choose key metrics that measure both sustainability performance and business results. Have systems in place to gather, examine, and report data with efficiency. Make metrics both meaningful to stakeholders and decision-makers.
Develop governance arrangements
Allocate specific responsibility for sustainability performance at all levels of the organisation. Consider creating a sustainability committee or incorporating sustainability into current governance arrangements. Provide leadership visibility and commitment.
Integrate with business operations
Infuse sustainability considerations into key business processes such as product development, procurement, and capital deployment. Revise policies, procedures, and decision-making frameworks to incorporate sustainability priorities.
Build communications strategies
Develop focused communications plans for various stakeholder groups. Balance openness on challenges with the celebration of achievements. Leverage communications on sustainability to build your brand and positioning in the market.
Put in place continuous improvement mechanisms
Formalize routine review cycles to measure progress, learn from experience, and modify your strategy. Build feedback loops that gain insights from employees, customers, and other stakeholders to push continuous innovation.
Recommended Tools and Methods for Framework Implementation
Your sustainability framework becomes much more manageable with the proper tools and methods. Below are some real-world options available for businesses at different points in their sustainability journey:
Assessment and Planning Tools
Impact Assessment
An open-source tool that assists in measuring your firm's social and environmental footprint through a detailed assessment system.
Future-Fit Business Benchmark
Offers a transparent, science-driven starting point to grasp what real sustainability can mean for your company.
Materiality Assessment Templates
Assist in ranking sustainability concerns by stakeholder importance and business relevance.
Statistical Process Control
Applies statistical techniques to measure process performance and detect variations that signify inefficiency.
Measurement and Reporting Systems
Greenhouse Gas Protocol
The benchmark for measuring and reporting emissions through tools and calculators for all businesses.
Sustainability Management Software
Solutions such as Sphera or Measurabl that automate data capture, analysis, and reporting.
Life Cycle Assessment Tools
Assist in analyzing the environmental effects of products across their lifecycle.
Simulation Modelling
Produces computer models of your operations to experiment with improvement scenarios prior to applying them in the actual world.
Stakeholder Engagement Methods
AA1000 Stakeholder Engagement Standard
Offers a structure for quality stakeholder engagement.
Design Thinking Workshops
Joint workshops that involve the stakeholders in creating sustainable solutions.
Sustainability Advisory Panels
Institutionalized vehicles for regular stakeholder input and feedback.
Implementation Frameworks
Science-Based Targets initiative (SBTi)
Assists businesses in establishing emission reduction targets based on climate science.
Circular Economy Business Models
Structural designs for rethinking operations so as to prevent waste and pollution.
ISO 14001
A global standard for environmental management systems that can be coupled with growth plans.
Common Pitfalls in Building Sustainable Business Frameworks
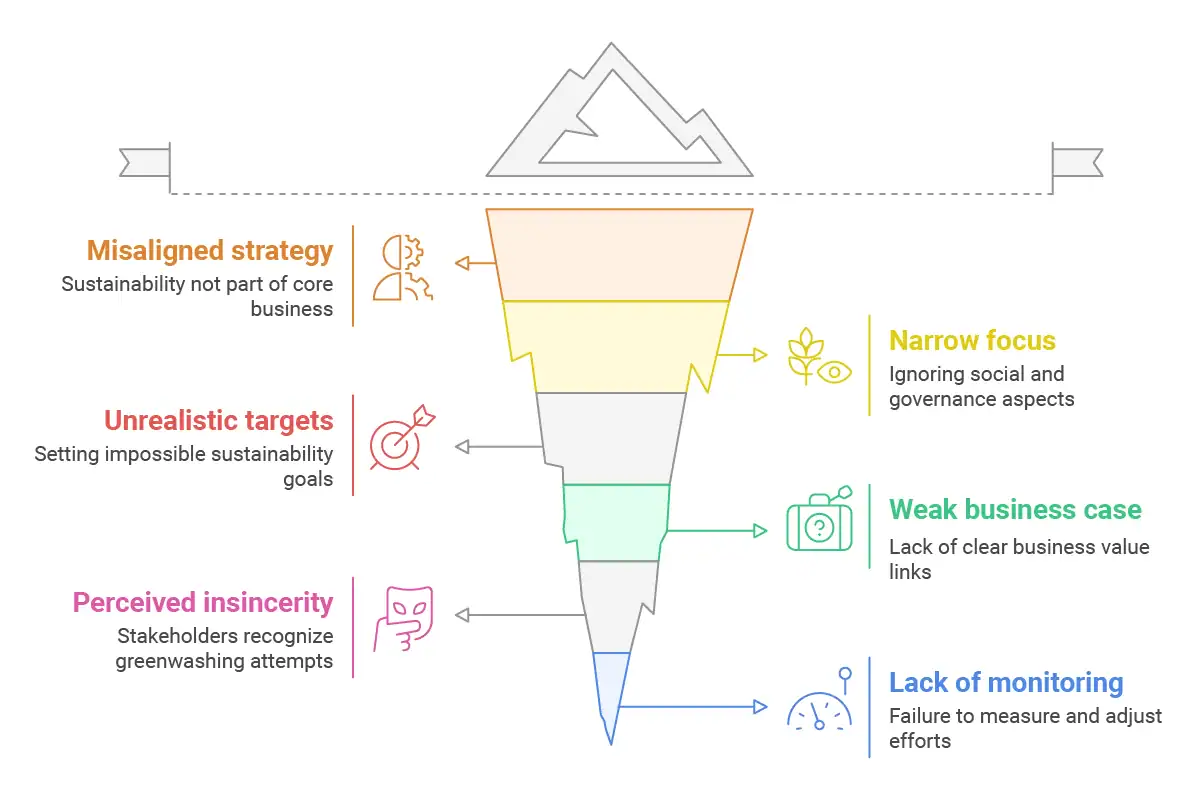
Even sustainable initiatives well-intended can fail without a thoughtful plan. Steer clear of these framework development mistakes:
Treating sustainability as distinct from core strategy
Sustainability efforts that are not aligned with business strategy tend to remain underfunded side projects that do not achieve significant impact or growth value.
Looking only at the environmental side
Numerous companies fall into the trap of defining sustainability solely in terms of environmental responsibility without considering social and governance considerations that can be just as relevant to stakeholders and business resilience.
Having unrealistically high aims
High aims can motivate, but obviously impossible targets undermine credibility and motivation. Make sure your sustainability goals challenge your organisation but are achievable based on your resources and capabilities.
Overlooking the business case
Sustainability projects must ultimately deliver business value. If there are no clear links to cost savings, revenue increases, risk reductions, or other business objectives, sustainability programs find it difficult to survive when the environment changes.
Conveying insincerity
Stakeholders are quick to recognize the difference between sincere commitment and “greenwashing.” Exaggeration of achievements or the making of unsubstantiated statements erodes trust and can result in serious damage to reputation.
Not measuring and not adjusting
Sustainability is not an end goal, but rather a path. Organizations that do not regularly monitor performance and modify strategy based on outcomes are likely to stagnate or lose their way from the sustainability journey in the long run.
Moving from Compliance to Competitive Advantage

The most effective sustainable companies go through distinct stages of maturity, each with growing potential for expansion and distinction:
Stage 1: Compliance-Oriented Sustainability
Here, companies concentrate mainly on addressing regulatory demands and industry benchmarks. Although this method reduces legal exposure, it provides limited competitive advantage and can be costly without returns.
Stage 2: Efficiency-Oriented Sustainability
As companies grow up, they start looking at ways to save and turn them into bottom-line impacts through sustainability practices such as energy efficiency, waste minimization, and process optimisation. This enhances the margins and builds some differentiation but remains a relatively limited perspective on sustainability.
Stage 3: Strategic Sustainability
At this point, sustainability gets linked to business strategy. Firms align sustainability with market direction, consumer choice, and competition. This strategy produces more robust growth through improved reputation, talent, and innovation.
Stage 4: Transformative Sustainability
The most evolved companies leverage sustainability as a prism for reframing their whole business model. They create products and services that address environmental or social issues, generate mutual value with stakeholders, and revolutionize conventional industry methods. This disruptive strategy realizes the highest growth potential while making meaningful contributions to sustainability issues.
To ascend this maturity ladder, companies must:
- Transition from reactive to proactive sustainability management
- Stretch their time horizon from short to long
- Widen their frame from narrow compliance to systemic influence
- Shift sustainability from a cost centre to a value creator
Firms that are able to make this shift find themselves with more robust business models, improved stakeholder relationships, and greater opportunity for profitable growth—a classic illustration of the power of marketing management strategies to deliver real competitive advantage.
Business Benefits of an Integrated Sustainability Framework
A holistic sustainability framework, when well applied, provides quantifiable business advantages that benefit scalable growth in direct ways:
Financial Performance
- Cost saving: Sustainable business tends to consume less and waste less, saving direct costs.
- Revenue increase: Sustainable products tend to attract premium prices and new market segments.
- Investment attraction: Preferential terms of investment increasingly accrue to businesses with strong sustainability.
- Risk reduction: Sustainable companies risk fewer regulatory fines, supply chain breakages, and reputational crises.
Market Position
- Brand differentiation: Sustainability promises enable brands to differentiate themselves in saturated markets.
- Customer loyalty: Sustainability practices foster stronger customer relationships and higher retention.
- Market growth: Sustainability innovations tend to create entry points for entirely new customer groups or markets.
- First-mover advantage: Firms that pioneer sustainability in their sector tend to create hard-to-succeed-against competitive positions.
Operational Excellence
- Innovation catalyst: Sustainability constraints tend to force creative problem-solving and innovation.
- Supply chain resilience: Sustainable supply chain practices minimize exposure to disruption.
- Improvements in productivity: Sustainability efforts often identify opportunities for efficiency that enhance productivity.
- Quality improvement: The rigor of sustainability management tends to result in better product and service quality.
Organisational Capacity
- Hiring talent: Good sustainability reputation facilitates hiring, particularly of younger talent.
- Employee engagement: Substantial sustainability efforts enhance employee engagement and productivity.
- Cultural strength: Mutual commitment to sustainability enables more cohesive, mission-driven cultures.
- Leadership development: Challenges to sustainability foster critical leadership skills such as systems thinking, stakeholder management, and long-term orientation.
Final Thoughts
Creating a business sustainability framework that drives scalable growth isn’t something you do overnight—it’s a revolution in the way you think about business strategy and operations. By weaving sustainability principles into your core business model, you build resilience that rides out market cycles and sets your brand up for sustained success.
The best frameworks strike a balance between short-term business necessities and longer-term priorities, creating value for all stakeholders while keeping the resources and relationships your business relies on intact. Balanced thinking converts what many see as limitations into drivers of innovation, differentiation, and growth.
As market expectations shift further, companies with strong sustainability systems will find themselves with more and more competitive edges—from preferred access to capital and people to enhanced customer loyalty and business resilience. Those who are not adapting risk falling behind as regulations get stronger, resource scarcity mounts, and stakeholder expectations build.
Need Help With Your Operational Efficiency?
Creating and applying a successful sustainability framework takes a broad range of expertise—from environmental science through stakeholder engagement to change management. If you want to speed your sustainability journey and maximise business gains, try working with experts who are familiar with both sustainability concepts and the dynamics of business growth.
Our experts assist small, medium, and large businesses in creating customised sustainability frameworks that resonate with their strategic goals, organisational culture, and resource limitations. From initial evaluation to implementation assistance, we offer down-to-earth advice that turns sustainability from a compliance mechanism into a compelling growth engine.
